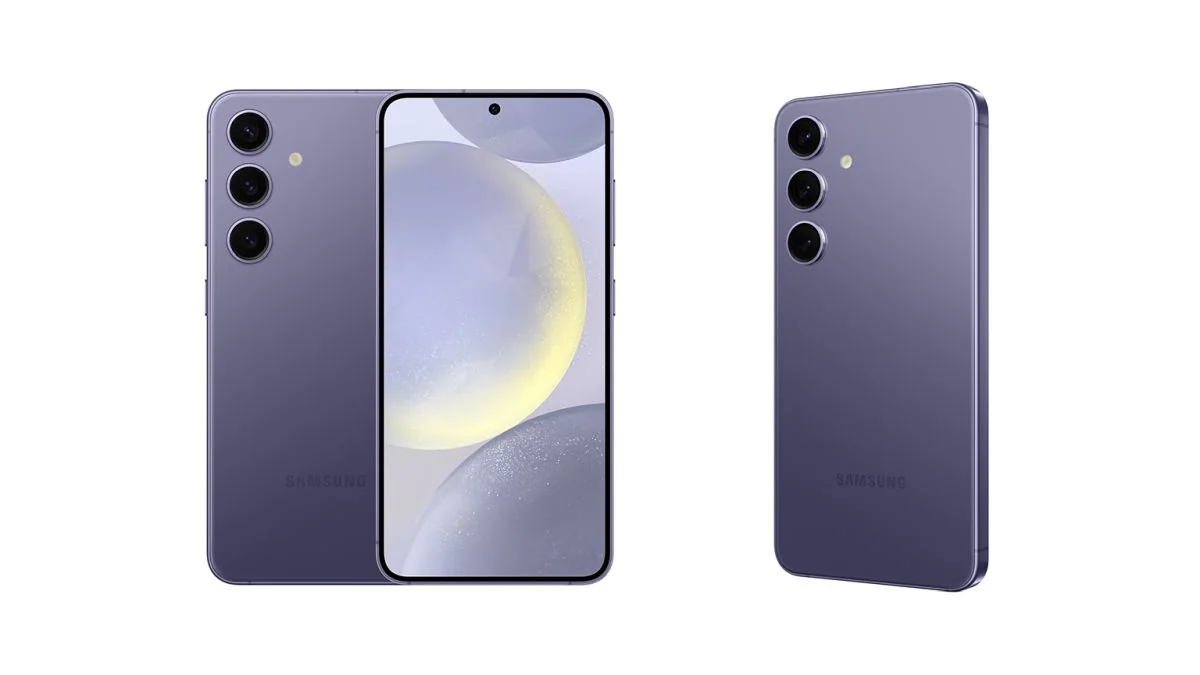
Samsung appears to have had a change of heart with their latest flagship lineup, the Galaxy S25 series. Addressing one of the major criticisms of the S24, Samsung is finally fixing the storage inadequacy that has been a sore point for users.
Galaxy S25 Series: Enhanced performance with faster UFS 4.0 storage
The Galaxy S25 will start with a minimum of 256GB, ditching the outdated 128GB option. This upgrade doubles the storage and enhances performance by adopting the faster UFS 4.0 standard over the previously used UFS 3.1 in the 128GB models.
Read also: Introducing the Samsung Galaxy S24 FE: A feature-rich Smartphone for every fan
All models in the S25 series are set to feature 12GB of RAM as standard, with the Ultra variant offering an option for 16GB RAM in higher storage configurations. This ensures that even the base model of the S25 can handle complex AI features onboard, bolstering its future-proofing.
Galaxy S25 Series release date: What to expect from Samsung’s unpacked event
The much-anticipated Galaxy Unpacked event, where the S25 series will be unveiled, is scheduled for January 22nd. According to South Korean media reports, fans eager to receive the new devices must wait until February 7th for deliveries to start.
The buzz around the S25 lineup also includes a new model, informally dubbed the “S25 Slim.” This variant is incredibly thin, measuring between 6 and 7 mm, potentially making it one of the slimmest flagship phones on the market.
However, with such a slim profile, battery life is a concern. Samsung hopes not to follow in Apple’s footsteps with a significantly reduced battery, ideally aiming for at least 4,500mAh to compensate for the thin design.
Read also: Why Redmi 13 is a perfect buy for smartphone users on a budget
Samsung Galaxy S25 production: Will the S25 Slim be a limited edition model?
The S25 Slim will see a relatively low production run of just 3 million units, indicating Samsung might be testing consumer response before possibly scaling up production based on demand.
Interestingly, leaks regarding the Galaxy F16, a budget offering from Samsung, have shown a camera design that might inspire future S-series models. If adopted for the S26, this design could set a new trend. The S25 lineup will debut with One UI 7, introducing new features that significantly enhance user experience.